Embark on a journey through the realm of Reliable IT automation tools for system administration, where efficiency and reliability converge to streamline processes and enhance productivity.
Discover the key aspects and functionalities that define these essential tools in the digital landscape.
Overview of Reliable IT Automation Tools
IT automation tools are software solutions designed to streamline and simplify repetitive tasks in system administration. These tools help automate various processes, such as software deployment, updates, monitoring, and maintenance, saving time and reducing human errors.
Using reliable IT automation tools is crucial for system administrators to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and consistency in managing IT infrastructure. Reliable tools help improve productivity, enhance security, and minimize downtime, ultimately leading to cost savings and better performance.
Common Features in Reliable IT Automation Tools
- Centralized Management: Ability to manage multiple systems from a single interface, simplifying administration tasks.
- Scalability: Capability to scale up or down based on the organization's needs without compromising performance.
- Security: Robust security features to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Integrations: Seamless integration with other IT systems and applications for a cohesive workflow.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Real-time monitoring of system performance and detailed reporting for analysis and optimization.
Examples of Reliable IT Automation Tools

IT automation tools play a crucial role in system administration by simplifying repetitive tasks and improving efficiency. Below are some popular IT automation tools used in the industry:
1. Ansible
Ansible is an open-source automation tool that focuses on simplicity and ease of use. It uses SSH to connect and automate tasks across multiple servers. Ansible is suitable for configuration management, application deployment, and orchestration.
2. Puppet
Puppet is another widely used configuration management tool that allows administrators to define infrastructure as code. It uses a declarative language to manage configurations and enforce desired states on systems. Puppet is suitable for large-scale environments with complex configurations.
3. Chef
Chef is a powerful automation platform that uses a domain-specific language to define system configurations. It follows a model-driven approach and can be used for continuous automation, infrastructure management, and compliance automation.
4. SaltStack
SaltStack, also known as Salt, is a scalable and flexible automation tool that uses a master-minion architecture for remote execution. It is suitable for managing cloud infrastructure, event-driven automation, and configuration drift detection.
5. PowerShell
PowerShell is a task automation framework from Microsoft that allows system administrators to automate tasks and manage systems using a command-line shell and scripting language. It is particularly useful for Windows environments and integrates well with other Microsoft products.
6. Terraform
Terraform is an infrastructure as code tool that allows users to define and provision infrastructure using declarative configuration files. It supports multiple cloud providers and helps automate the creation, updating, and deletion of resources in a consistent manner.
Implementation Strategies for IT Automation Tools
Implementing IT automation tools in a system administration environment requires careful planning and execution to ensure seamless integration and optimal efficiency. Here are the steps involved in implementing IT automation tools, best practices for integrating them into existing workflows, and tips for optimizing their use:
Steps for Implementing IT Automation Tools
- Assess Needs: Identify repetitive tasks that can be automated to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
- Choose the Right Tool: Select an IT automation tool that aligns with your organization's requirements and goals.
- Plan Implementation: Develop a detailed implementation plan outlining timelines, resources, and responsibilities.
- Training and Testing: Provide training to staff on how to use the automation tool effectively and conduct thorough testing before full deployment.
- Gradual Rollout: Implement automation in phases to minimize disruptions and ensure smooth transition.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the performance of the automation tool and make adjustments as needed to optimize results.
Best Practices for Integrating Automation Tools
- Collaboration: Involve all stakeholders in the implementation process to ensure buy-in and successful adoption.
- Standardization: Establish standardized procedures and workflows to maximize the benefits of automation across the organization.
- Security: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and systems from potential risks associated with automation.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of automation processes and configurations for future reference and troubleshooting.
Tips for Optimizing the Use of Automation Tools
- Regular Updates: Keep automation tools up-to-date with the latest features and security patches to ensure optimal performance.
- Customization: Tailor automation workflows to meet specific business needs and adapt to changing requirements.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Implement monitoring tools to track the performance of automation processes and generate reports for analysis and optimization.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourage feedback from users and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement and enhance the efficiency of automation tools.
Security Considerations for IT Automation
When utilizing automation tools in system administration, it is crucial to prioritize security to safeguard sensitive data and prevent potential security breaches.
Importance of Security in IT Automation
- Automation tools often have access to critical systems and data, making them attractive targets for cyber attacks.
- Security breaches through automation tools can lead to data loss, downtime, financial losses, and damage to the organization's reputation.
- Ensuring security in IT automation helps in maintaining compliance with regulations and standards.
Common Security Risks with IT Automation Tools
-
Insecure Credentials:
Storing passwords and credentials insecurely can lead to unauthorized access to systems and data.
-
Unencrypted Data:
Transmitting sensitive data in plain text exposes it to interception by malicious actors.
-
Insufficient Access Controls:
Poorly configured access controls can result in unauthorized users gaining access to automation workflows.
Strategies for Securing Automation Workflows
-
Implement Encryption:
Encrypt data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
-
Use Secure Credentials Management:
Utilize secure vaults or key management services to store and manage sensitive credentials securely.
-
Regularly Audit Access Controls:
Conduct regular audits to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to automation workflows.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Automation Processes
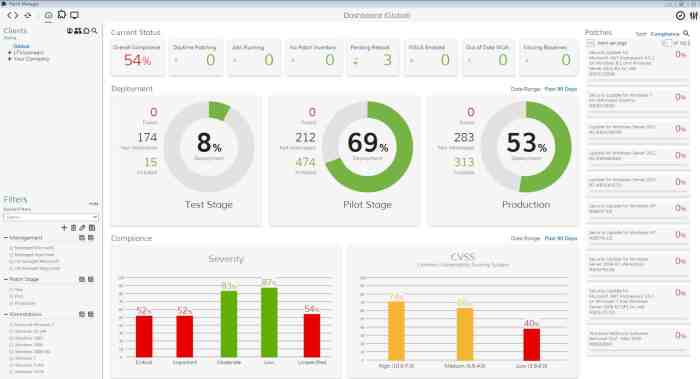
Monitoring and troubleshooting automation processes play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of automated tasks within an IT environment. By actively monitoring and promptly addressing any issues that arise, system administrators can maintain the reliability and efficiency of automation tools.
Monitoring Automated Processes
Monitoring automated processes involves regularly checking the status of scheduled tasks and workflows to confirm that they are executing as intended. This can be achieved through the use of monitoring tools that provide real-time visibility into the performance of automation processes.
Key metrics to monitor include task completion rates, error logs, resource utilization, and overall system health.
- Set up alerts: Configure alerts within monitoring tools to notify administrators of any deviations from expected behavior or performance thresholds.
- Review logs: Regularly review logs generated by automation tools to identify any errors or issues that may require troubleshooting.
- Track performance: Monitor the performance of automated tasks over time to detect any trends or patterns that may indicate underlying problems.
Troubleshooting Automation Issues
When issues occur during automation processes, it is essential to troubleshoot and resolve them promptly to minimize disruptions and maintain system reliability. Common troubleshooting methods include:
- Identify the root cause: Analyze error messages and logs to pinpoint the exact cause of the issue.
- Test individual components: Isolate different components of the automation process to identify the specific area where the problem is occurring.
- Implement temporary fixes: Apply temporary workarounds to keep automated tasks running while a permanent solution is developed.
Role of Monitoring Tools
Monitoring tools are instrumental in maintaining the reliability of automation processes by providing visibility and insights into the performance of automated tasks. These tools enable system administrators to:
- Proactively identify issues: Detect potential problems before they escalate and impact system operations.
- Optimize performance: Analyze data collected by monitoring tools to optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of automation processes.
- Ensure compliance: Monitor automated tasks to ensure they adhere to regulatory requirements and internal policies.
Last Word
As we conclude our exploration of Reliable IT automation tools for system administration, we are left with a profound understanding of how these tools revolutionize system management, paving the way for seamless operations and optimized workflows.
Key Questions Answered
What are IT automation tools?
IT automation tools are software applications that help streamline and automate various tasks within a system administration environment, reducing manual effort and improving operational efficiency.
Why is using reliable tools important for system administration?
Reliable tools ensure consistency, accuracy, and security in system administration processes, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
What are some common features to look for in reliable IT automation tools?
Common features include scalability, flexibility, robust security measures, user-friendly interfaces, and compatibility with existing systems.
How can one monitor automated processes effectively?
Monitoring tools can be used to track the performance of automated processes, alerting administrators to any issues or anomalies that may arise.
What strategies can be employed to secure automation workflows?
Implementing encryption, access controls, regular audits, and keeping software updated are effective strategies to enhance the security of automation workflows.